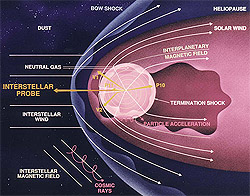
I want to show you three old views of the Universe.
These images are outdated but still relevant basically.
Still good science.
The First image is
The Virgo Supercluster
The local group of galaxies is just one of many centered around the massive Virgo Cluster.
Earth (and the Sun) are in the Virgo Supercluster so it is our view center.
Collectively, all of these groups and clusters form a unit known as the Virgo Supercluster shown here.
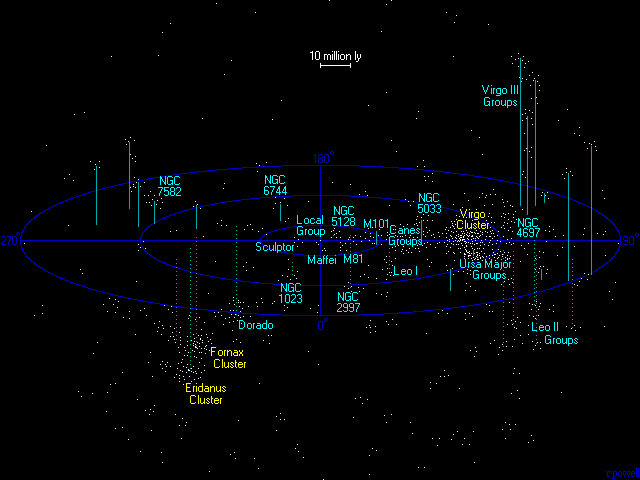
Number of galaxy groups within 100 million light years = 200
* Number of large galaxies within 100 million light years = 2500
* Number of dwarf galaxies within 100 million light years = 50 000
* Number of stars within 100 million light years = 200 trillion
Our galaxy is just one of thousands that lie within 100 million light years. The above map shows how galaxies tend to cluster into groups, the largest nearby cluster is the Virgo cluster a concentration of several hundred galaxies which dominates the galaxy groups around it. Collectively, all of these groups of galaxies are known as the Virgo Supercluster. The second richest cluster in this volume of space is the Fornax Cluster, but it is not nearly as rich as the Virgo cluster. Only bright galaxies are depicted on the map, our galaxy is the dot in the very centre.
The second image is our
Supercluster Neighbors
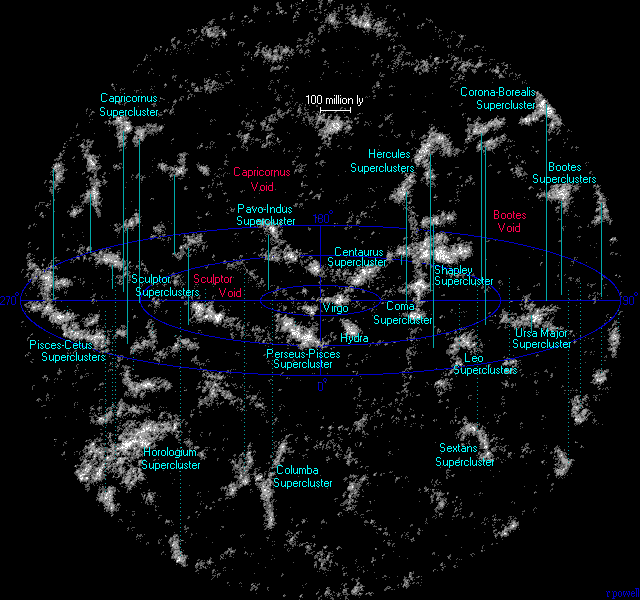
Number of superclusters within 1 billion light years = 100
* Number of galaxy groups within 1 billion light years = 240 000
* Number of large galaxies within 1 billion light years = 3 million
* Number of dwarf galaxies within 1 billion light years = 60 million
* Number of stars within 1 billion light years = 250 000 trillion
Galaxies and clusters of galaxies are not uniformly distributed in the Universe, instead they collect into vast clusters and sheets and walls of galaxies interspersed with large voids in which very few galaxies seem to exist. The map above shows many of these superclusters including the Virgo supercluster - the minor supercluster of which our galaxy is just a minor member. The entire map is approximately 7 percent of the diameter of the entire visible Universe.
Finally a representation of the
Universe.
Notice how it is a ball?
Its a ball because that is the limit of our ability to look not the limit of the Universe. Its a view from our relative perspective only.
The Universe within 14 billion Light Years
The Visible Universe
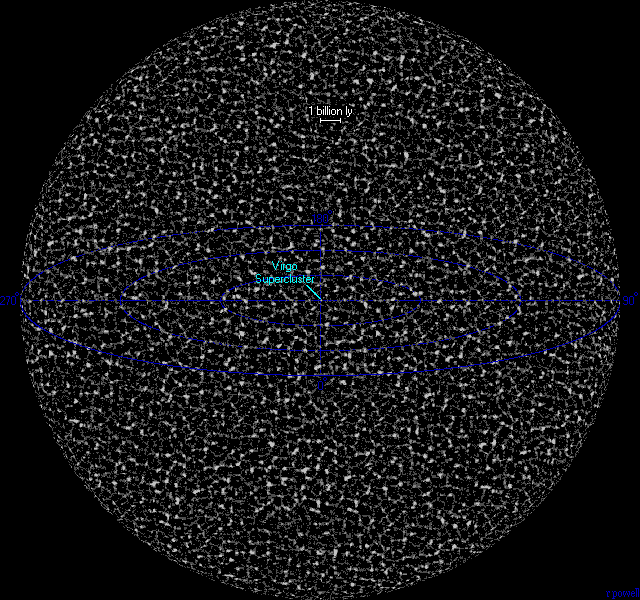
Number of superclusters in the visible universe = 10 million
* Number of galaxy groups in the visible universe = 25 billion
* Number of large galaxies in the visible universe = 350 billion
* Number of dwarf galaxies in the visible universe = 7 trillion
* Number of stars in the visible universe = 30 billion trillion (3x10²²)
This map attempts to show the entire visible Universe. The galaxies in the universe tend to collect into vast sheets and superclusters of galaxies surrounding large voids giving the universe a cellular appearance. Because light in the universe only travels at a fixed speed, we see objects at the edge of the universe when it was very young up to 14 billion years ago.
Here is the source page:
http://www.atlasoftheuniverse.com/
I think the most current scope of the Universe is in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey.
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey has created the most detailed three-dimensional maps of the Universe ever made, with deep multi-color images of one third of the sky, and spectra for more than three million astronomical objects. Learn and explore all phases and surveys—past, present, and future—of the SDSS.
Here is the Link:
http://www.sdss.org/
One thing is sure.
The Universe is vast and complex, far exceeding mankind's wildest imaginations. What we don't know far, far exceeds what we do.
So, anything is possible given the scope. Even God.
Here is a cool video that takes you for a ride.
JOURNEY TO THE EDGE OF THE (observable) UNIVERSE w/ Alec Baldwin
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bVQpwxgMQCg
But, the Universe is not only immensely big, it is also immensely small.
Powers of Ten (1977)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MzEp1caAJdQ
Science has already made this video obsolete. Its still accurate but limited in scope for what we know now.